Computer Network Defined

A computer network is a set of computers connected
together for the purpose of sharing resources. The most common resource shared
today is connection to the Internet. Other shared resources can include a
printer or a file server.
A
computer network is a group of computer systems and other computing hardware
devices that are linked together through communication channels to facilitate
communication and resource-sharing among a wide range of users. Networks are
commonly categorized based on their characteristics.A computer network is
a set of connected computers. Computers on a network are called nodes.
The connection between computers can be done via cabling, most commonly the
Ethernet cable, or wirelessly through radio waves. Connected computers can
share resources, like access to the Internet, printers, file servers, and
others. A network is a multipurpose connection, which allows a single computer
to do more.
Types of Network Connections
Computer networks can be
broken down historically into topologies, which is a technique of
connecting computers. The most common topology today is a collapsed
ring. This is due to the success of a network protocol called the Ethernet.
This protocol, or a network language, supports the Internet, Local Area
Networks, and Wide Area Networks.
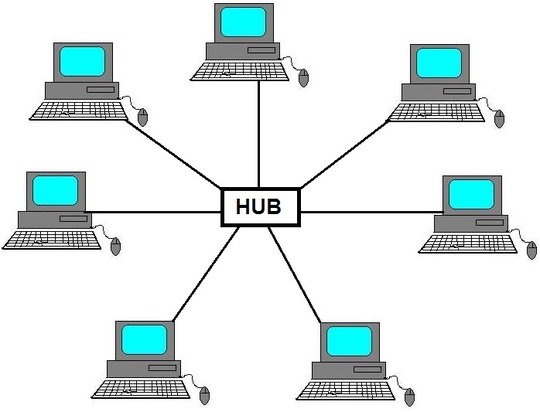 Star Topology
Star Topology
A star topology is
a design of a network where a central node extends a cable to each computer on
the network. On a star network, computers are connected independently to the
center of the network. If a cable is broken, the other computers can operate
without problems. A star topology requires a lot of cabling.
 Bus Topology
Bus Topology
A bus topology is
another type of design where a single cable connects all computers and the
information intended for the last node on the network must run through each
connected computer. If a cable is broken, all computers connected down the line
cannot reach the network. The benefit of a bus topology is a minimal use of
cabling.
Collapsed Ring Topology
A similar topology is called
a ring. In this design, computers are connected via a single cable,
but the end nodes also are connected to each other. In this design, the signal
circulates through the network until it finds the intended recipient. If a
network node is not configured properly, or it is down temporarily for another
reason, the signal will make a number of attempts to find its destination.
A collapsed ring is
a topology where the central node is a network device called a hub, a router,
or a switch. This device runs a ring topology internally and features plugins
for cables. Next, each computer has an independent cable, which plugs into the
device. Most modern offices have a cabling closet, or a space
containing a switch device that connects the network. All computers in the
office connect to the cabling closet and the switch. Even if a network plug is
near a desk, the plug is connected via a cable to the cabling closet.
 Mesh Topology
Mesh Topology
A network setup where each
computer and network device is interconnected with one another, allowing for
most transmissions to be distributed, even if one of the connections go down.
This topology is not commonly used for most computer networks as it is
difficult and expensive to have redundant connection to every computer.
However, this topology is commonly used for wireless networks. Below is a visual example
of a simple computer setup on a network using a mesh topology.
 TREE Topology
TREE Topology
It has a root node and all
other nodes are connected to it forming a hierarchy. It is also called
hierarchical topology. It should at least have three levels to the hierarchy.
 HYBRID Topology
HYBRID Topology
It is two different types of
topologies which is a mixture of two or more topologies. For example if in an office
in one department ring topology is used and in another star topology is used,
connecting these topologies will result in Hybrid Topology (ring topology and
star topology).
Advantage
of Computer networks
•
Sharing of Devices such as printer and scanner
•
Sharing program / software
•
Sharing files
•
Sharing data
•
Sharing information
•
Sharing of single high-speed internet connection
•
Better communication using internet services such
as email, mailing list and internet Relate chat (IRC)
Disadvantage
of Computer Network
•
The larger network becomes, the more difficult it
is to manage.
•
If the network stops operating system, then it may
not be possible to access various resources
•
Computer Viruses: If any computer
system in a network gets affected by computer virus, there is a possible
threat of other systems getting affected too.
Types
of Network
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
is high speed network that connect local area network in Metropolitan Area such
as city or town and handles bulk of communication activity across the
region.
 A MAN typically includes one or more LAN but covers
a smaller geographically area than a WAN.
A MAN typically includes one or more LAN but covers
a smaller geographically area than a WAN.
Wide Area Network (WAN) is
a network that covers a large geographically area such country or the world. WAN
combines many types of media such as telephone lines, cables and radio wave.
Network
Architecture
Network Architecture is the overall design of a
computer network that describes how a computer network is configured and what
strategies are being used. It also known as network model or network design.
 Ethernet Cabling
Ethernet Cabling
You’ll need a sufficient number of Ethernet cables to connect all
devices in your network. Most modern networks use Category 5 or 6 cabling, and
you can purchase the cables in a variety of lengths. You can even buy cables in
different jacket colors to distinguish network devices in a large network. For
instance, you can use blue cables for PCs, red ones for servers, and so on.
Modem
 Your ISP usually provides a modem when you sign up for service,
although you can usually purchase your own from a list of approved devices if
you choose. A modem exists at the edge of your network and provides bidirectional
communication between your ISP and the devices inside your network. Modems come
in various forms depending on your service. A DSL modem, for example, connects
to your ISP via a telephone line, while a cable modem uses a coaxial link. Most
modems also have one or more Ethernet ports that you can use to connect the
device to a router, switch, or directly to a computer.
Your ISP usually provides a modem when you sign up for service,
although you can usually purchase your own from a list of approved devices if
you choose. A modem exists at the edge of your network and provides bidirectional
communication between your ISP and the devices inside your network. Modems come
in various forms depending on your service. A DSL modem, for example, connects
to your ISP via a telephone line, while a cable modem uses a coaxial link. Most
modems also have one or more Ethernet ports that you can use to connect the
device to a router, switch, or directly to a computer.
Routers and Switches
 A router or switch connects to your modem via an Ethernet cable
and provides connectivity to multiple devices. Unlike switches, routers enable
you to connect two networks together. For example, if you have one or more
branch offices, you can use a VPN-enabled router to provide a secure connection
to those offices. Routers and switches with a DSU/CSU provide T1 links to branch
offices. Routers have built-in firewalls and advanced features such as Web
filtering. Switches are mainly used for facilitating communication within a
single office network, although some contain such router-like features as the
ability to create virtual local area networks (VLANs). You can also purchase
unmanaged switches that need no configuration and work right out of the box.
A router or switch connects to your modem via an Ethernet cable
and provides connectivity to multiple devices. Unlike switches, routers enable
you to connect two networks together. For example, if you have one or more
branch offices, you can use a VPN-enabled router to provide a secure connection
to those offices. Routers and switches with a DSU/CSU provide T1 links to branch
offices. Routers have built-in firewalls and advanced features such as Web
filtering. Switches are mainly used for facilitating communication within a
single office network, although some contain such router-like features as the
ability to create virtual local area networks (VLANs). You can also purchase
unmanaged switches that need no configuration and work right out of the box.
Mac Address
-
hardware address
-
It is hardwired or hard-coded onto your computer's network interface card (NIC)
and is unique to it
Communication Devices
 1.
Hub
1.
Hub
- A non-intelligent device,
and has no decision making capability
- Take the input data from
one of the ports and broadcast the information to all the other ports connected
to the network.
2.
Repeaters
 - A repeater is a device similar to the Hub,
but has additional features.
- A repeater is a device similar to the Hub,
but has additional features.
- Used in places where amplification of input
signal is necessary
- Regenerates Faded Signals
3.
Switch
- A switch is an intelligent device
 - Has a decision making capacity
- Has a decision making capacity
4.
Bridges
- A device that connects
two local-area networks (LANs), or two segments of the same LAN that use the
same protocol
5.
Routers
- A router is a device that forwards
data packets along networks. A router is connected to at least two networks,
commonly two LANs or WANs or a LAN and its ISP's network.
6.
NIC(Network Interface Card)
- So that the computer can be
connected to a network.
